Alleviation: An International Journal of Nutrition, Gender & Social Development, ISSN 2348-9340 Volume 1, Number 1 (2014), pp. 1 - 8
© Arya PG College, Panipat & Business Press India Publication, Delhi
www.aryapgcollege.com
A Comparative Study on Awareness of Risk Factors Leading to Cardiovascular Heart Diseases among College Going Girls in Haryana
Dr. Santosh Tikoo, Ms Meenu, Ms.Sonam
Head,Project Fellow,Lecturer
Department of Home Science
Arya P.G. College, Panipat (Haryana), India
Email: dr.santoshtikoo@yahoo.in
Introduction
Life style diseases result due to our way of living. Life style diseases are also known as the diseases of civilization or longevity. Cardiovascular heart diseases are the major life style diseases leading to morbidity and mortality. There are many factors that lead to cardiovascular heart diseases e.g. diabetes, hypertension, physical inactivity, poor nutrition, obesity, mental stress and alcohol etc. Awareness of risk factors leading to these diseases is essential. However there is little information on awareness of cardiovascular heart diseases, so the present study was undertaken with the following objectives in mind:
• To assess the awareness of college going girls about risk factors leading to cardiovascular heart diseases.
• To find out the nutritional strategies to be followed to prevent cardiovascular heart diseases.
Following hypotheses were also formulated
• There is no association between awareness and location of residence of college going girls.
• There is no association between awareness and class of study of college going girls.
Methodology
The study was conducted in Arya P.G. College. Total sample size was 60 girl students (30 from undergraduate and 30 from postgraduate classes). Data were collected through questionnaire. Girl students were the key informants. Data were coded according to the code numbers assigned. Frequencies and percentages were calculated. Chi-square was applied to test association between variables.
Results and Discussion
Age of the College Going Girls
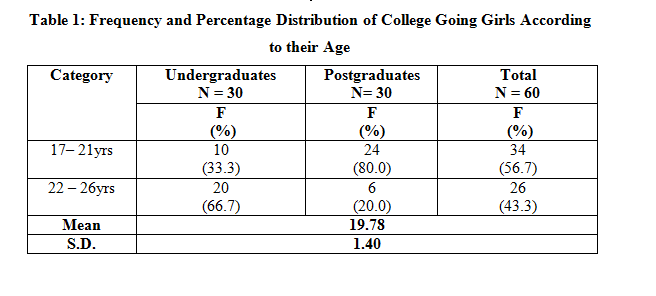
As is evident from Table 1 that majority of the college going girls (56.7%) fell in the age category of 17-21 years whereas 43.3 per cent were in the age category of 22-26 years. It can be seen from the table that college going students were quite young.
Location of Residence
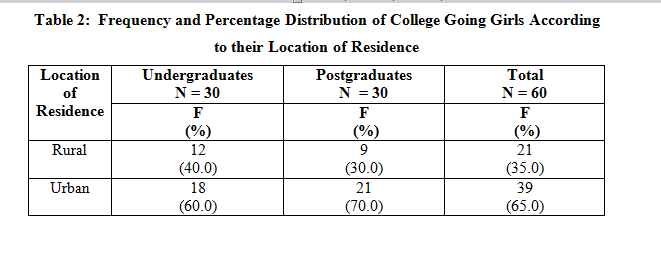
Table 2 portrays that majority of the college going girls (65%) belonged to urban areas with maximum percentage from postgraduate classes (70%) whereas 35 per cent belonged to rural areas
Subject of Study of College Going Girls
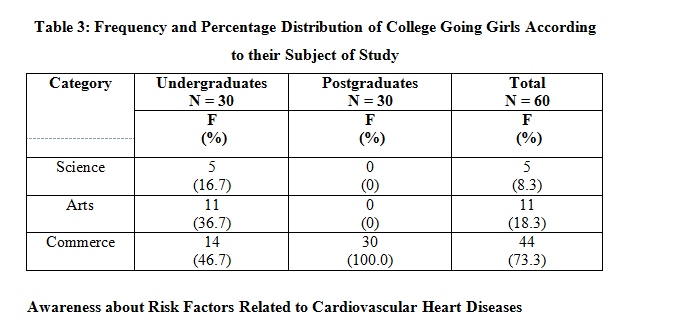
It can be observed from Table 3 that maximum percentage of the sample respondents (73.3%) were from commerce stream with cent percent of the sample from post graduate classes. There were 18.3 per cent of the students who belonged to art faculty whereas only 8.3 per cent of the students were from science background.
It was reported by 88.3 per cent of the students that mental stress and depression affect heart (Table 4). There were 81.7 and 78.3 per cent of the students who reported negative to the statements that smoking has no affect on heart disease and heart disease is a male disease respectively. Seventy-five per cent of the students responded no to the statement that neck, shoulder, upper back or abdominal discomforts have no relation with heart problems whereas an equal percentage were aware that stroke/high blood pressure/heart attack/ atherosclerosis are four main types of cardiovascular diseases. There were 73.3 per cent of the respondents who responded negative to the statement that over weight/obesity/high blood pressure do not contribute to heart diseases. There were 68.3 per cent of the respondents who were aware that silent heart attacks are especially common in diabetes. Nearly 67 per cent responded no to the statement that diabetes does not increase the risk of heart diseases whereas 65 per cent were of the view that 10 – 20 pounds of weight loss often improves the blood cholesterol and triglycerides.
Table 4 Frequency and Percentage Distribution of College Going Girls According to their Awareness about Risk Factors Related to Cardiovascular Heart Diseases
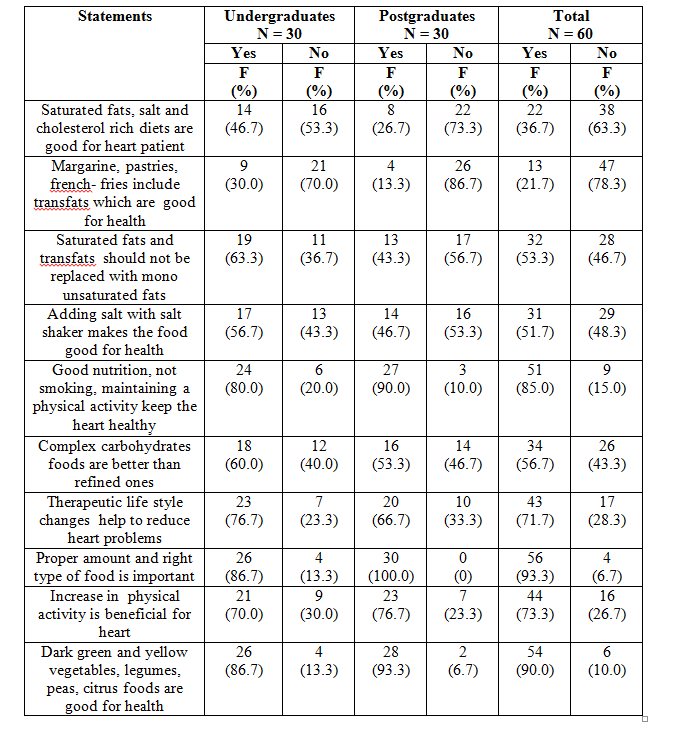
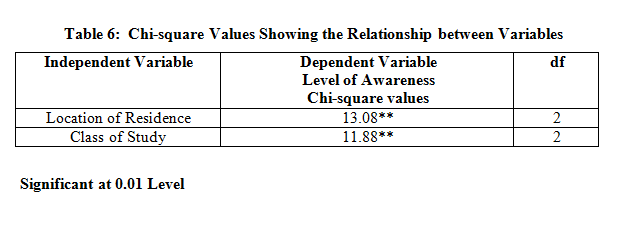
Chi-square test was applied and it was found that there was significant association between awareness and location of residence (Chi-square =13.08, Sig. at 0.01 level) and class of study of the students (Chi-square value = 11.88, Sig. at 0.01 level). Thus the null hypotheses were rejected. It can be concluded that level of awareness was more among urban and post graduate students.
Conclusion
The study suggested that awareness education about risk factors leading to cardiovascular diseases is more needed among rural and undergraduate students in the college.
References
Bremer JC (1983) Metabolism and Functions. Physiological Review 63:1420.
Johari P (2006) Fats and Proteins. New Delhi: Sonali Publications.
John S, Parimalam SR, Karthiga S and Chellappa AR (2005) Nutrition and Dietetics. Chennai: Tamilnadu Textbook Corporation.

